Ginger Beer Nutrition Facts A Comprehensive Guide
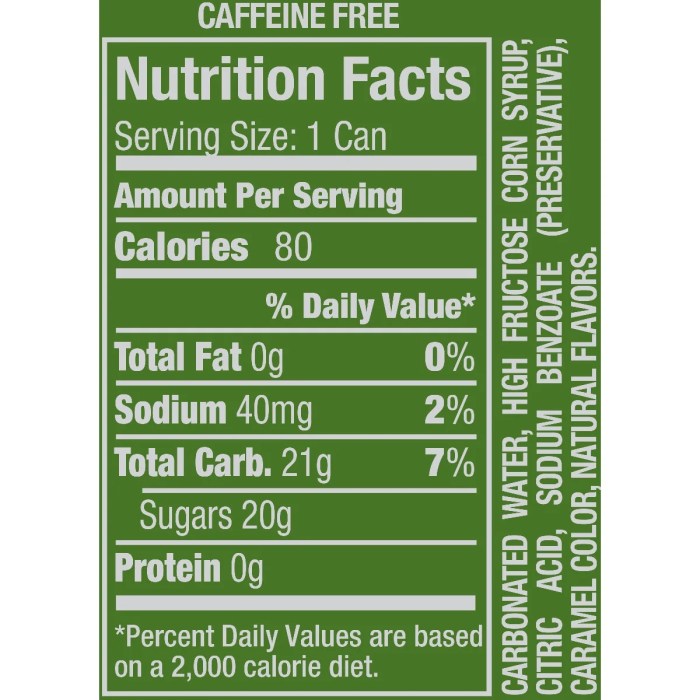
Nutritional Content of Ginger Beer
Ginger beer nutrition facts – Ginger beer, a fermented beverage with a spicy kick, offers a refreshing alternative to other carbonated drinks. However, its nutritional profile varies depending on the brand and ingredients used. Understanding the macronutrient composition and potential health benefits associated with its vitamins and minerals is crucial for making informed choices.
Macronutrient Profile of Ginger Beer
The macronutrient content of ginger beer primarily consists of carbohydrates, with minimal protein and virtually no fat. The sugar content is a significant component of the carbohydrate profile and varies considerably across brands. While some brands may opt for natural sweeteners like cane sugar or honey, others utilize high-fructose corn syrup or other artificial sweeteners. This directly impacts the overall caloric value.
Understanding ginger beer nutrition facts involves considering its sugar content and potential health benefits. A comparison with the fat content and nutritional profile of other oils can be insightful, such as examining the avocado oil nutrition facts for a contrasting perspective. Returning to ginger beer, it’s important to note its relatively low caloric density compared to many other beverages.
Below is a table illustrating the nutritional variation amongst some popular brands (note that this data is representative and may vary slightly depending on the batch and source).
| Brand Name | Serving Size (mL) | Carbohydrates (g) | Sugar (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | 330 | 25 | 22 |
| Brand B | 355 | 30 | 28 |
| Brand C | 250 | 18 | 15 |
| Brand D (Organic) | 300 | 20 | 18 |
Vitamins and Minerals in Ginger Beer and Their Health Benefits
Ginger beer, particularly varieties made with real ginger, offers a small amount of certain vitamins and minerals. The quantities are generally modest, but contribute to overall dietary intake.The presence of these nutrients depends heavily on the ingredients and brewing process. For example, a ginger beer made with fresh ginger root will contain a higher concentration of these beneficial compounds than one made with ginger extract or flavorings.
- Gingerol: A potent antioxidant with anti-inflammatory properties. It’s associated with benefits for digestive health and may help alleviate nausea.
- Vitamin C: A powerful antioxidant that supports immune function and collagen production.
- Potassium: Essential for maintaining fluid balance and supporting healthy blood pressure.
- Magnesium: Plays a vital role in muscle function, nerve transmission, and blood sugar control.
Comparison with Other Carbonated Beverages, Ginger beer nutrition facts
Compared to other carbonated beverages like colas and other sodas, ginger beer generally contains less artificial coloring and flavoring. However, its sugar content can be similar or even higher depending on the brand. Diet versions of ginger beer may contain artificial sweeteners, presenting a different set of potential health considerations. In contrast to plain carbonated water, ginger beer provides additional flavor and some vitamins and minerals, but also significantly more calories and sugar.
Therefore, moderation is key regardless of the type of carbonated beverage consumed.
Impact of Ginger Beer on Health
Ginger beer, while a refreshing beverage, derives its distinctive flavor and potential health benefits primarily from ginger. Understanding the impact of ginger beer on health requires considering both the positive attributes of ginger and the potential drawbacks introduced through processing and added ingredients.Ginger’s anti-inflammatory properties are well-documented. Studies suggest that gingerol, a bioactive compound in ginger, can help reduce inflammation throughout the body.
This can be beneficial for managing conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, although it’s crucial to remember that ginger beer is not a replacement for medical treatment. Furthermore, ginger has been traditionally used to aid digestion, potentially relieving symptoms of nausea, bloating, and indigestion. However, the effectiveness of ginger in these contexts depends on various factors, including the concentration of ginger and individual responses.
Ginger’s Anti-inflammatory and Digestive Effects
The anti-inflammatory effects of ginger are primarily attributed to gingerol and other related compounds. These compounds work by inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators, thus reducing pain and swelling. For digestion, ginger stimulates the production of saliva and gastric juices, improving the breakdown and absorption of food. It can also help relax the muscles of the digestive tract, easing the movement of food through the system and alleviating symptoms of indigestion.
However, the amount of ginger in commercial ginger beer can vary significantly, affecting the actual health benefits received. Some brands may use only a small amount of ginger extract, limiting the potential health advantages.
Potential Drawbacks and Risks of Consuming Ginger Beer
The consumption of ginger beer, particularly in large quantities, presents some potential risks. It’s important to be aware of these factors before making it a regular part of your diet.
- High Sugar Content: Many commercial ginger beer brands contain significant amounts of added sugar, contributing to weight gain, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and other health problems associated with high sugar intake. The sugar content can vary widely depending on the brand and type of ginger beer.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Some brands opt for artificial sweeteners to reduce sugar content. While lower in calories, the long-term health effects of artificial sweeteners are still under investigation, and some individuals may experience digestive discomfort or other adverse reactions.
- Potential Interactions with Medications: Ginger has blood-thinning properties. Individuals taking anticoagulant medications (like warfarin) or those with bleeding disorders should consult their doctor before consuming significant amounts of ginger beer, as it could potentially increase the risk of bleeding.
- Acidity: The acidity of ginger beer can irritate sensitive stomachs or exacerbate existing gastrointestinal conditions in some individuals.
The Role of Added Sugars and Artificial Sweeteners
The sugar content in ginger beer significantly impacts its nutritional profile and potential health effects. Many brands rely heavily on added sugars, such as sucrose or high-fructose corn syrup, to enhance flavor and sweetness. This added sugar contributes to the overall calorie count and can negatively affect blood sugar levels, leading to potential health risks. In contrast, some manufacturers use artificial sweeteners like aspartame or sucralose to reduce the sugar content and calories.
However, concerns remain regarding the potential long-term health effects of artificial sweeteners, prompting ongoing research and debate. Consumers should carefully examine the nutritional labels of different ginger beer brands to make informed choices based on their individual health goals and preferences. Choosing brands with lower added sugar content or opting for naturally sweetened varieties is generally recommended.
Ginger Beer and Dietary Considerations

Ginger beer, while offering a refreshing taste and potential health benefits, requires careful consideration within a balanced diet and for individuals with specific dietary needs. Understanding its nutritional profile and potential interactions with existing health conditions is crucial for safe and informed consumption.
Sample Daily Meal Plan Incorporating Ginger Beer
A balanced daily meal plan incorporating ginger beer can be easily achieved. The key is to consider ginger beer as a beverage choice, not a meal replacement, and to pair it with meals that complement its flavor profile and nutritional content. The following is a sample plan, adaptable to individual preferences and dietary needs:
Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries and a sprinkle of nuts, paired with a small glass (around 8 ounces) of ginger beer. The fiber in the oatmeal and antioxidants in the berries balance the sugar content in the ginger beer.
Lunch: A large salad with grilled chicken or fish, various vegetables, and a light vinaigrette dressing. A small glass of ginger beer can complement this meal, offering a refreshing contrast to the savory flavors.
Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted vegetables (broccoli, carrots, sweet potatoes). This provides a balanced source of protein and vitamins. Ginger beer is less suitable with this meal, but a cup of herbal tea could be a good alternative.
Snacks: A small handful of almonds or a piece of fruit. Ginger beer is not typically recommended as a snack.
Ginger Beer and Specific Dietary Restrictions
The suitability of ginger beer for individuals with specific dietary restrictions depends heavily on the brand and its ingredients. Always check the nutritional label carefully.
Diabetes: Many ginger beers are high in sugar, which can negatively impact blood sugar levels. Individuals with diabetes should either choose sugar-free varieties or consume ginger beer sparingly, carefully monitoring their blood glucose levels. They should also consider the overall carbohydrate content of their diet.
Gluten Intolerance: Most commercially produced ginger beers are naturally gluten-free, as they are typically made from water, ginger, sugar, and yeast. However, always check the label to ensure that no gluten-containing ingredients have been added during processing or as preservatives. Some brands may use malt, which contains gluten.
Choosing a Healthier Ginger Beer
Selecting a healthier ginger beer requires careful examination of the nutritional label. Prioritize the following:
- Lower Sugar Content: Look for brands with lower grams of sugar per serving. Compare different brands to find options with the least added sugar.
- Natural Ingredients: Opt for ginger beers made with natural ingredients, avoiding artificial sweeteners, colors, and preservatives. The shorter the ingredient list, the better.
- Calorie Count: Be mindful of the calorie content, especially if you are watching your weight. Compare calorie counts across various brands.
- Serving Size: Pay attention to the serving size indicated on the label. A smaller serving size can help you control your overall sugar and calorie intake.
Visual Representation of Nutritional Information: Ginger Beer Nutrition Facts

Visual representations are crucial for effectively communicating the nutritional content of ginger beer. Charts and graphs offer a clear and concise way to understand the complex interplay of macronutrients and compare different brands. This section will explore effective visual methods for presenting this information.
Macronutrient Composition of Ginger Beer Using a Pie Chart
A pie chart is an excellent choice for illustrating the proportions of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in a typical serving of ginger beer. To create this chart, first determine the percentage contribution of each macronutrient based on the nutritional information provided on the ginger beer label. For example, if a serving contains 10g of carbohydrates, 0g of protein, and 0g of fat, and the total calories are based primarily on carbohydrates (approximately 4 calories per gram), the carbohydrate percentage would be calculated as follows: (10g
- 4 calories/g) / (Total Calories)
- 100%. Protein and fat percentages would be calculated similarly. Once the percentages are determined, each segment of the pie chart would represent a macronutrient, sized proportionally to its percentage contribution. The chart should be clearly labeled with the name of each macronutrient and its corresponding percentage. A legend explaining the color coding of each segment should also be included.
For instance, carbohydrates might be represented by a light brown segment, protein by a dark brown segment, and fat by a yellow segment.
Comparison of Sugar Content Across Different Ginger Beer Brands Using a Bar Graph
A bar graph is ideal for comparing the sugar content of various ginger beer brands. To construct this graph, list the different brands along the horizontal axis (x-axis). The vertical axis (y-axis) would represent the amount of sugar in grams per serving. Each brand would be represented by a bar, with the height of the bar corresponding to its sugar content.
The sugar content data should be obtained from the nutrition labels of each brand. For example, if Brand A contains 15g of sugar per serving, Brand B contains 10g, and Brand C contains 20g, the bars representing these brands would be of different heights reflecting these values. The graph should include a clear title, such as “Sugar Content Comparison of Various Ginger Beer Brands,” a labeled x-axis (“Ginger Beer Brand”), and a labeled y-axis (“Sugar Content (grams per serving)”).
Each bar should be clearly labeled with the brand name and its corresponding sugar content. A key might not be necessary as the labels are clear.
FAQs
Is ginger beer good for digestion?
Ginger, a key ingredient, possesses anti-inflammatory properties and may aid digestion for some individuals. However, the effects can vary.
Does ginger beer contain caffeine?
Generally, no. However, always check the specific brand’s ingredients list as some might contain added caffeine.
Can I drink ginger beer if I’m pregnant?
Moderate consumption is generally considered safe, but it’s best to consult your doctor, especially if you have any existing health concerns.
Are there low-sugar options available?
Yes, many brands now offer low-sugar or sugar-free varieties, often using artificial sweeteners. Check nutrition labels carefully.
Is ginger beer suitable for people with diabetes?
Due to its sugar content, it’s best consumed in moderation by individuals with diabetes. Opt for low-sugar or sugar-free options and monitor blood sugar levels.